Blog
AMA: How do AMRs make smart, real-time decisions independently?
Autonomy software is an autonomous mobile robot’s (AMR) onboard intelligence that enables the robot to perceive its environment, make decisions in real-time, and safely navigate dynamic facilities—all without human intervention. Autonomy software allows the robot to reach its destination and complete its job by taking the best route, at the fastest possible speed, without compromising safety—even as it adapts to unexpected obstacles along the way.
Learn more about how autonomy software differentiates AMRs from AGVs in this blog.
How does autonomy software enable AMRs to make smart, precise decisions in real-time?
AMR autonomy software is made up of two core domains: perception and navigation.
Perception refers to how the robot uses its sensors to build an understanding of its environment. It’s made up of three key functions:
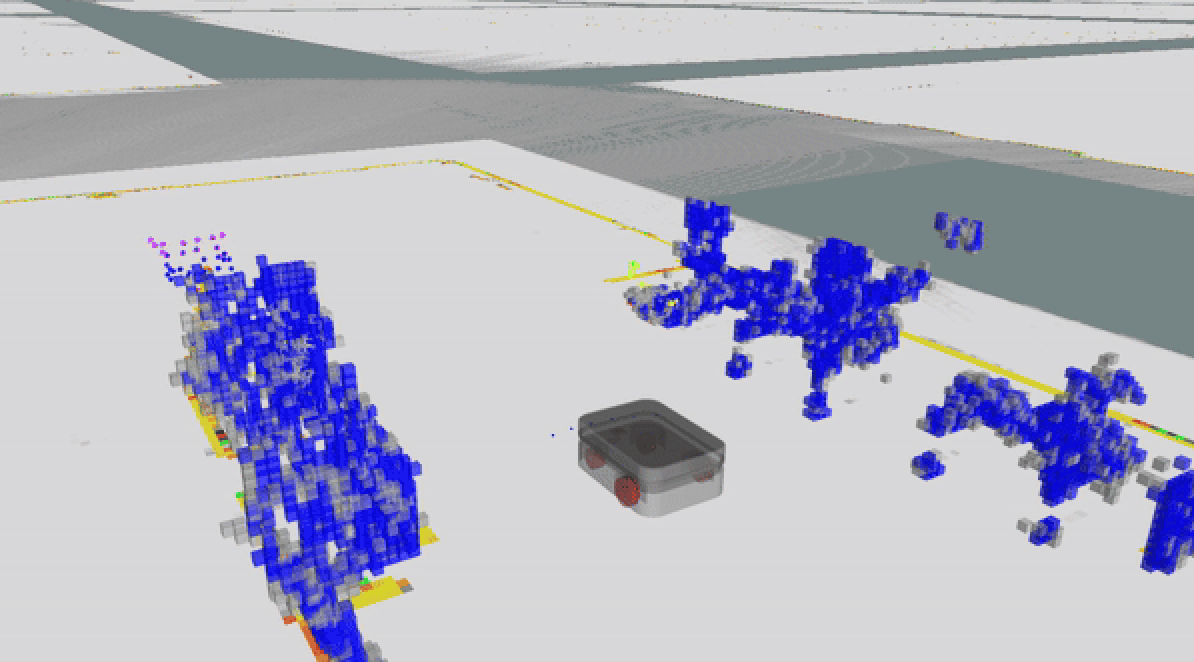
- Sensing: This is how the robot sees. In this step, a variety of onboard sensors—including LiDARs, 3D cameras, wheel encoders and more—gather data about the environment to help the robot make safe, efficient decisions.
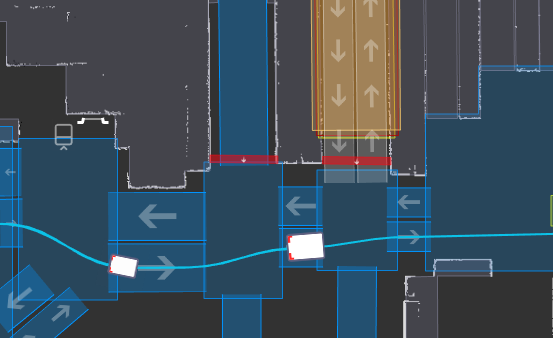
- Mapping and localization: This is how the robot perceives its position in the facility. The first step during deployment set-up is to drive a robot around the facility, creating a structured representation of the environment. Once operations are active, the robot will continuously use this map to reference its location in real-time.
- Understanding the scene: This is how the robot interprets what it sees. Sensor data is continuously analyzed to identify nearby obstacles and interactive elements. This allows the robot to make decisions about how to safely and accurately navigate, especially during endpoint tasks like docking, charging, or picking up carts—where precise positioning is critical.

Image 1: Safety-rated LiDARs provide precise, long-range detection of environments and obstacles.
Navigation refers to how the robot uses the understanding from perception to make decisions and take action independently. It comprises three key processes:
- Planning: This is how the robot intends to reach its destination. Based on its environment and assigned jobs—as well as traffic rules and current payload—the AMR creates a high-level plan to reach its destination, optimizing for the quickest path.
- Controlling the robot: This is how the robot safely executes on its plan. Autonomy controls the robot hardware—with knowledge of its safety fields and real-time perception insights—to make progress towards the destination as efficiently, safely, and smoothly as possible.
- Adapting to real-time obstacles: This is how the robot autonomously determines a new route when there is a person or blockage on its expected path. This may mean simply diverting around the obstacle, or turning around and finding an entirely new route.

Video 1: Autonomy software enables AMRs to make real-time decisions and navigate autonomously around expected and unexpected obstacles.
Curious to learn more about how autonomy software works? Watch the webinar to see a live demonstration of the process behind making smart, precise decisions in real time.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Stay in the loop on product news, case studies, upcoming events and more.