Blog
Manufacturing risk management with flexible automation

Industry 4.0 technologies deliver opportunity for manufacturers to manage risks using flexible automation, particularly when it comes to material movement inside facilities. Automation capabilities are now adaptable, scalable and intelligent, delivering actionable operational insights via data that may have not been tracked or available before.
Manufacturing risk management is facing a number of new challenges such as cybersecurity, unfamiliar technologies, and customer demand for customization. Yet technology, particularly those delivered within the realm of Industry 4.0, can alleviate these symptoms by boosting operational efficiency, integrating into properly configured networks, cybersecurity defence, enhancing productivity and keeping plant workers safer.
Flexible technology and risk management
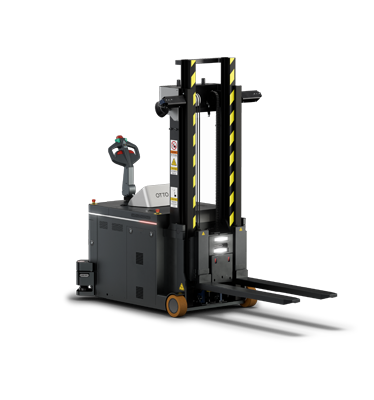
One new technology includes autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) that break free of magnetic strips and pre-programmed routes, unlike their autonomous guided vehicle (AGV) brethren. These robotic vehicles, designed for material movement activities, don’t require infrastructure and, instead, are able to adapt to new environments to deliver an easily integrated and scalable solution powered by Industry 4.0.

Photo credit: archersafetysigns.co.uk
AMRs eliminate risks associated to downtime. Compared to autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs), AMRs continuously move through the plant, are programmed to avoid obstacles and help to keep all links of the intralogistic supply chain operational at all times. They also allow manufacturers to re-allocate human capital to higher-value work in the plant, while in turn improving safety in the plant. For example, AMRs are able to replace forklifts in a variety of applications as they can take on the long-distance material transport tasks more efficiently, and safely collaborate with floor personnel. Furthermore, these technologies enable data acquisition capabilities that provide actionable information about their processes. This is a particularly important factor: a manufacturer now has the ability to use data analytics to develop a digital trust to successfully implement digital enterprise applications.
A Canadian manufacturer of warehouse furniture implemented collaborative robots in its facility to improve labour productivity. Workers were manually loading large press brakes with heavy metal brakes – a physically straining task. Introducing human-robot collaboration allows humans and machines to work in close proximity without any risk to the workers. A built-in force control automatically slows down or pauses if there’s any contact with human workers. McKinsey & Co. suggests the manufacturer was able to increase throughput and increase sales by 40% while maintaining its employee base and reducing plant injuries.
Data drives decision-making

Photo credit: govexec.com
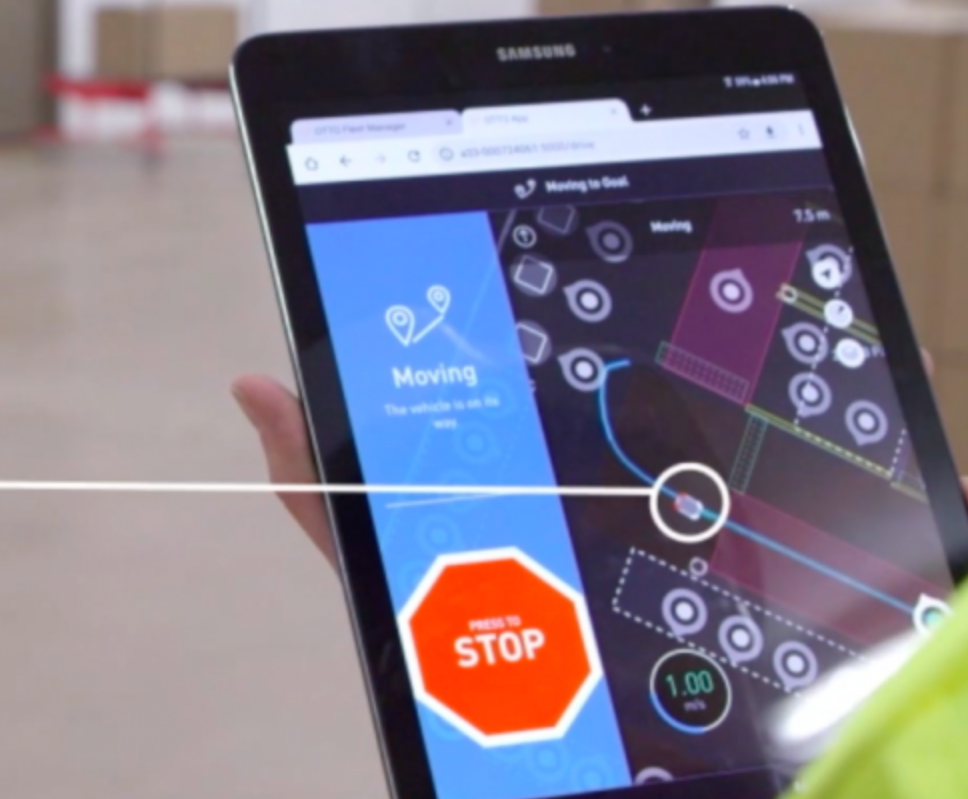
Indeed, early adopters on these implementations are using data analytics to help drive decision-making, including those involved in the manufacturing risk management process. A PwC report suggests the relationship between a strong risk management process and robust data integrity systems can help manufacturers better manage cybersecurity breaches and other operational headaches.
While early industrial robots and autonomous technologies were best-suited to high-volume, low-variety applications, new sensor technologies and software developments are opening the robotic world to new applications, including those within autonomous material handling.
By leveraging supply chain analytics via data captured by autonomous material movement systems manufacturers are able to uncover ways to better predict demand during peak production seasons, trends in product development and optimizing their entire manufacturing and distribution networks. This is helping manufacturers to rethink decision-making activities and managing operational risk through the deployment of advanced, Industry 4.0 technologies.