Blog
The impact of automation on the logistics labor market

According to the 2023 MHI Industry Report, robotics and automation has the highest potential to disrupt the industry and one of the highest to create a competitive advantage. According to the report, "Robotics/Automation has become table stakes for operations to remain competitive." 14% of businesses have already adopted robotics and automation, and another ~80% are predicted to adopt the technology within the next five years.
While companies are eager to adopt this technology in their own facilities, workers are concerned about the impact automation will have on employment opportunities.
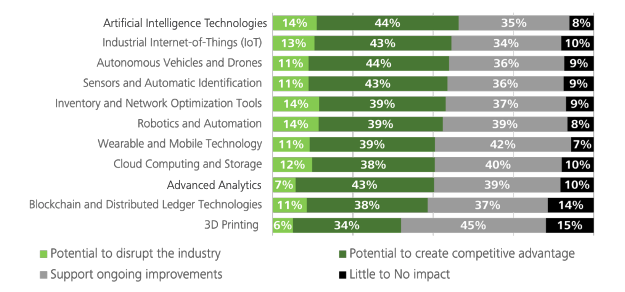
Chart 1: Adopting robotics and automation is likely to give companies a competitive advantage. The technology also has the highest potential to disrupt the market.
Repetitive tasks can be automated without job loss
There are very few jobs that can be fully automated, since the human brain is too valuable to replace in many situations. More likely, certain tasks within a job could be automated to ensure operations run more efficiently. In a typical job role, less than half (45%) of tasks can be automated since anything requiring extensive decision-making, problem-solving or communication skills, for example, is done best by people. Tasks that require these higher value-added skills, rather than the repetitive or boring ones that can be automated, are also the tasks that workers are most interested in performing.
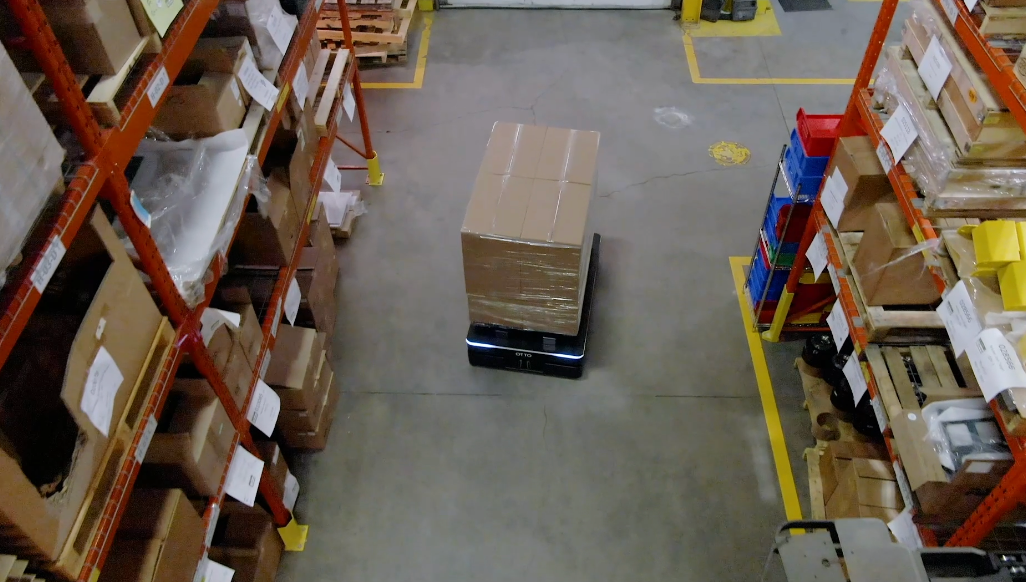
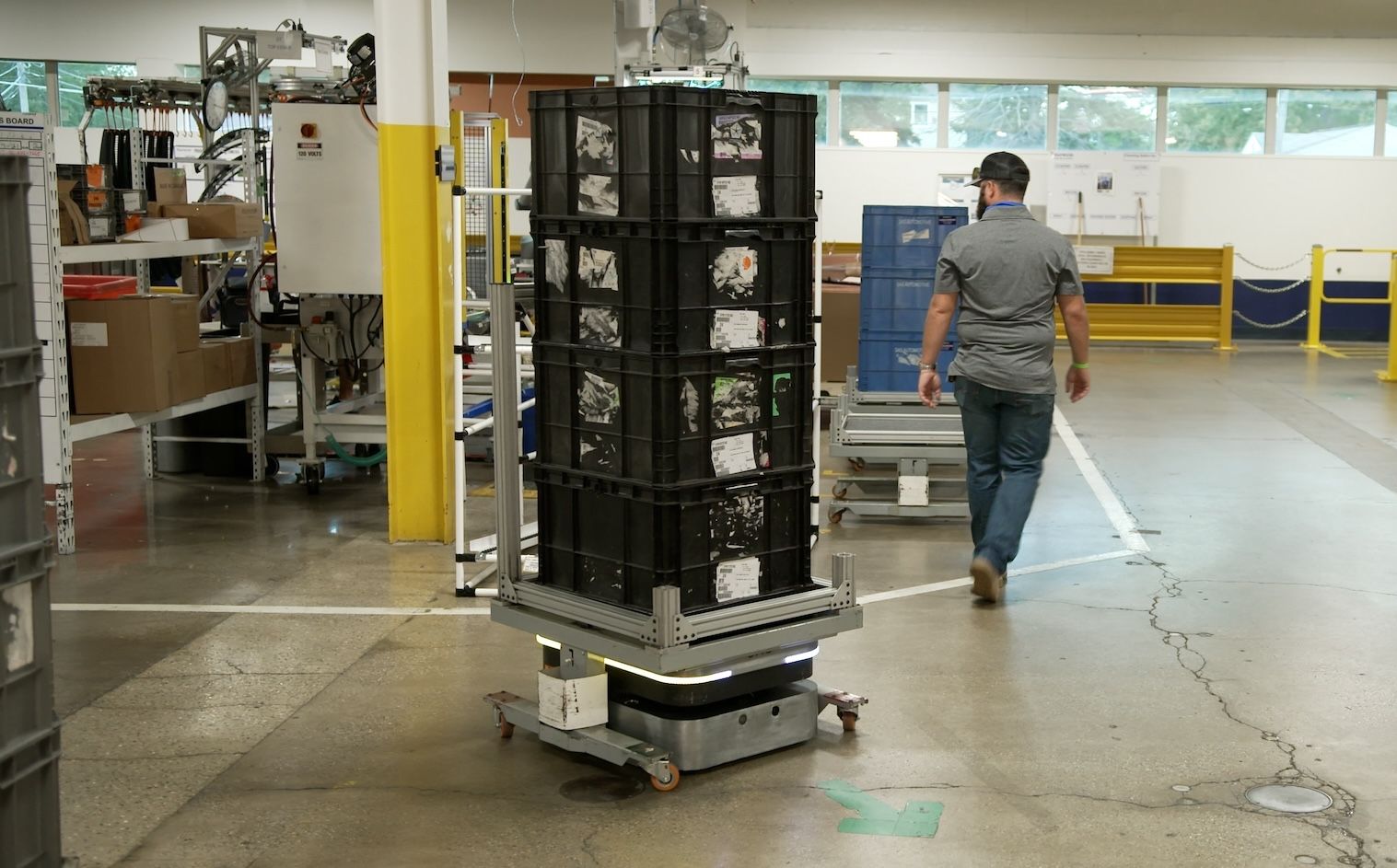
Most companies pursue policies of “collaborative automation” with robotics used to support people rather than replace them. Amazon, for example, has deployed more than 750,000 mobile robots and thousands of other robotic systems that help move, sort, identify, and package customer orders. During that time, Amazon has hired hundreds of thousands of employees to work in the operations as well.
Automation can support workers by doing repetitive, dull or dangerous activities that often add less value, but need to be done. Over 40% of workers spend at least a quarter of their work week on repetitive tasks, and nearly 60% estimate they could save six or more hours a week with automation. If repetitive tasks were automated, those workers say they would spend more time on value-added tasks (72%) and interesting or rewarding tasks (78%), increasing efficiency at and interest in work.
With that in mind, it becomes strikingly clear that organizations that invest in automation will be at a huge competitive advantage and be best prepared for the future of work.
Gene Farrell
Senior Vice President of Product, Smartsheet
Automation leads to new job roles
Along with assisting workers in the aspects of their jobs that are less valuable, automation also creates new work opportunities by generating demand for new, higher-skilled technical positions. For example, McKinsey & Company foresees a future where technological skills, both advanced IT skills and basic digital skills, will increase, driven by the need for greater creativity and complex information processing.
These higher skilled jobs created by automation are bringing higher pay as well. Examples of jobs created by automation include:
- Machine Learning Engineer: $128,032 per year
- Data Scientist: $124,074 per year
- Robotics Engineer: $89,872 per year
- Robot Technician: $67,421 per year
- Algorithm Engineer: $101,432 per year
Robots are optimizing production more than ever, increasing global competitiveness, and performing dull, dirty and dangerous tasks that enable companies to create higher-skilled, better-paying, and safer jobs where people use their brains, not their brawn.
Jeff Burnstein
President, A3
This switch toward higher-skilled, better-paying technical roles enabled by automation will ultimately result in higher net employment. According to Deloitte and the Manufacturing Institute, 4.8 million new manufacturing jobs are projected to be created by 2028.
Adoption of automation is becoming more and more common in warehouses and factories, but companies will always require human workers for the higher value-added tasks. If the greater efficiency and agility afforded by automation helps the logistics sector grow, so will demand for these emerging occupations.